Discover the Symptoms of your Enlarged Prostate
Discover the Symptoms of Your Enlarged Prostate
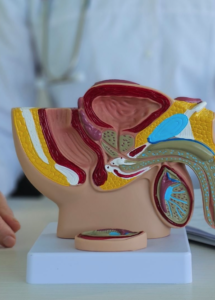
Understanding Enlarged Prostate (BPH): Causes, Symptoms, and Management
1. Enlarged Prostate (BPH):
BPH is a common condition that primarily affects men over the age of 50, although it can begin earlier.
The prostate gland, which produces fluid for semen, naturally grows throughout a man’s life.
Symptoms of an enlarged prostate include:
-
-
- Frequent and urgent urination.
- Troubles with urine stream.
- Incontinence and dribbling.
- Pain after urination.
- Urine remaining in the bladder.
-
-
- About 50% of men in their 50s and 60s experience symptoms, as do 90% of men aged 80 and older.
If you’re concerned about urinary changes, consult your doctor to rule out other issues and find ways to manage symptoms.
2. Remedies and Treatments for your Enlarged Prostate :
-
-
- Lifestyle changes, medications, and other treatments are available to manage BPH symptoms:
- Get Sufficient Exercise:
- Regular physical activity can benefit overall fitness and prostate health.
- Kegel exercises strengthen pelvic muscles and reduce urine dribbling.
- Slow Down When Urinating:
- Relax your muscles and allow time for delayed urine flow to empty the bladder completely.
- Incomplete bladder emptying due to an enlarged prostate can lead to complications.
- Medications:
- Take natural supplements and vitamins to support prostate health.
- Alpha blockers (e.g., Flomax, Rapaflo) relax bladder neck and prostate muscles.
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (e.g., Finasteride, Dutasteride) prevent hormonal changes and shrink the prostate.
- Procedures and Surgeries:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): Removes part of the prostate.
- Laser therapy: Uses laser beams to reduce prostate size.
- Prostate lift: Compresses the sides of the prostate.
- Embolization: Decreases prostate size by blocking blood supply.
- Open or robot-assisted prostatectomy: Removes the prostate through an incision on the lower abdomen.
- Get Sufficient Exercise:
- Lifestyle changes, medications, and other treatments are available to manage BPH symptoms:
-
3. Dietary Considerations:
-
-
-
-
- Foods rich in vitamin C and zinc may support prostate health.
- Avoid processed foods, caffeine, and spicy foods.
-
-
-
5 frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to enlarged prostate (BPH) and its management:
What causes an enlarged prostate?
FAQ 1. An enlarged prostate, or BPH, is primarily caused by age-related changes in the prostate gland. Hormonal imbalances, genetics, and lifestyle factors may also contribute.
It’s essential to understand that BPH is a common condition and not necessarily linked to prostate cancer.
FAQ 2. What are the common symptoms of BPH?
- Symptoms of an enlarged prostate include:
- Frequent urination (especially at night).
- Weak urine stream.
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination.
- Incomplete bladder emptying.
- Dribbling after urination.
- If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
FAQ 3. How can I manage BPH symptoms at home?
Lifestyle modifications can help:
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity supports overall health, including prostate health.
- Practice Kegel exercises: These strengthen pelvic muscles and improve bladder control.
- Take your time when urinating: Avoid rushing and allow the bladder to empty fully.
FAQ 4. What medications are used for BPH?
- Alpha blockers: These relax prostate and bladder muscles, improving urine flow (e.g., Flomax, Rapaflo).
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors: These reduce prostate size by blocking hormonal changes (e.g., Finasteride, Dutasteride).
- Natural Supplements: Build and maintain prostate function and health with natural supplements.
FAQ 5. What are the surgical options for BPH?
Surgical procedures may be necessary if symptoms are severe:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): Removes part of the prostate.
- Laser therapy: Uses lasers to shrink the prostate.
- Prostate lift: Compresses the prostate to improve urine flow.
- Embolization: Blocks blood supply to reduce prostate size.
- Prostatectomy: Surgical removal of the prostate.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any health condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.